Describe the Effects of the Oceans on Weather and Climate
In fact as we describe in research published in Nature CO 2 released by the oceans. Climate change ocean change.

Oceans Of The World Arctic Weather Weather And Climate Oceans Of The World
Climate change threatens coastal areas which are already stressed by human activity pollution invasive species and storms.

. The oceans and atmosphere store and exchange energy in the form of heat moisture and momentum. The ocean influences weather patterns by distributing heat and moisture around the globe. Increased greenhouse gases from human activities result in climate change and ocean acidification.
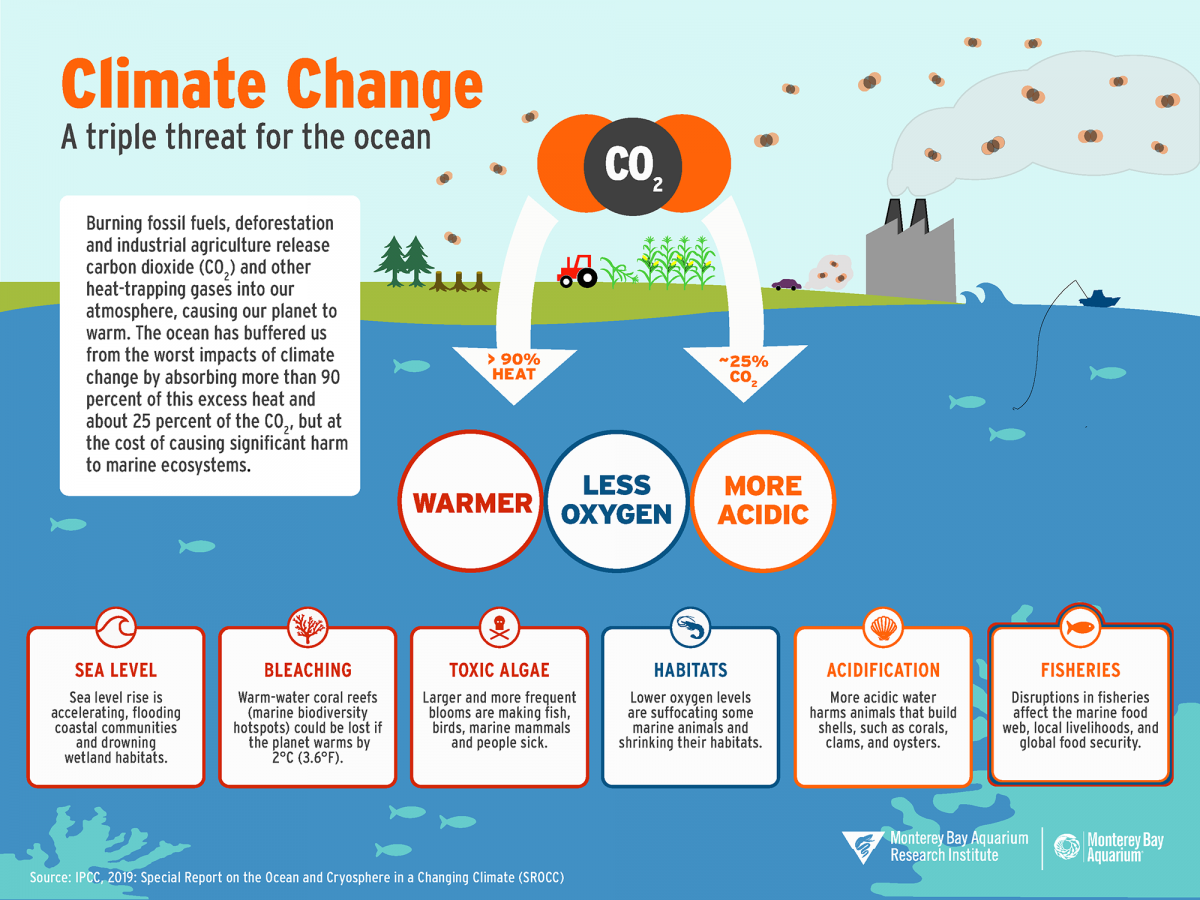
Warmer ocean waters spawn stronger hurricanes and other tropical storms and more evaporation leads to more intense rainfall. Coastal development reduces the ability of natural. The worlds ocean is a massive sink that absorbs carbon dioxide CO 2.
Sea level rise could erode and inundate coastal ecosystems and eliminate wetlands. The ocean is being disproportionately impacted by increasing carbon dioxide CO 2 and other greenhouse gas emissions GHG from human activities. Climate change is taking a toll on forests farms freshwater sources and the economy but ocean ecosystems remain the epicenter of global warming.
In fact the ocean represents over 70 of the Earths surface and contains 97 of all water on Earth. The oceans also regulate the global climate. Hurricane Wilma bears down on the Florida Keys.
Hurricanes Maria and Jose September 2017. They are also the worlds largest store of carbon where an estimated 83 of the global carbon cycle is circulated through marine waters. They also absorb heat more effectively than land and ice surfaces and store heat more efficiently than land.
Check out the major effects of warmer oceans on people and the environment. Plants Animals and Ecosystems. Warm ocean waters provide the energy to fuel storm systems that provide fresh water vital to all living things.
Climate change warms the ocean causing knock-on effects such as thermal expansion - which leads to a rise in sea level - and changes in ocean currents. The ocean also absorbs carbon dioxide from Earths atmosphere. Ocean current is a directed permanent or continuous movement of oceans water.
The melting of ice both on land and in the sea also affects the ocean causing more sea-level rise and reducing the salinity of the ocean respectively. As Earth warms water in the ocean soaks up energy heat and distributes it more evenly across the planet. The additional heat and carbon dioxide in the ocean can change the environment for the many plants and animals that live there.
Understanding and predicting precipitation is critical to farmers who decide which crops to plant and how deep based in part on soil moisture levels. Increased ocean acidity makes it more difficult for certain organisms such as corals and shellfish to build their skeletons and shells. Climate varies by region as a result of local differences in these interactions.
The movement of the ocean water is caused by forces acting on the water including the breaking waves salinity differences Coriolis effects the wind. This concept relates to the idea that climate is best understood from an Earth system perspective. The ocean stores heat like a fly wheel for climate.
This great reservoir continuously exchanges heat moisture and carbon with the atmosphere driving our weather patterns and influencing the slow subtle changes in our climate. Oceans have tremendously high heat capacity so they have a large damping effect on climate. The ocean is also very effective at absorbing and storing heat.
If you have spent time at the beach or in a coastal city you will likely appreciate the way in which the ocean affects the weather and climate of the coastal region. The oceans have tremendous thermal and dynamical inertia which can slow and dampen the rate of climate change. The majority of radiation from the sun is absorbed by the ocean particularly in tropical waters around the equator where the ocean acts like a massive heat-retaining solar panel.
Climate change dramatically affects coral reef ecosystems. Warmer oceans affect weather patterns cause more powerful tropical storms and can impact many kinds of sea life such as corals and fish. Although the oceans help reduce climate change by storing large amounts of carbon dioxide increasing levels of dissolved carbon are changing the chemistry of seawater and making it more acidic.
The warm and cold ocean currents play a major role in determining the climate of the coastal landmasses in their vicinity. Climate change leading to increases in ocean temperatures evaporation of seawater and glacial and sea ice melting could create an influx of warm freshwater onto the ocean surface. The impacts of changes in ocean currents on humanity could be severe as currents play a major role in maintaining Earths climate.
The ocean covers 70 of the global surface. The upper ten feet 3 meters of the ocean holds as much heat as the entire atmosphere. Ocean heat is concentrated near the surface because warm water is less dense than cold.
Just like the oceans affect weather patterns they play a major role in the Earths climate system. C overing more than 70 percent of the Earths surface and containing about 97 percent of its water the ocean is the Earths largest reservoir for moisture. Earths climate is influenced by interactions involving the Sun ocean atmosphere clouds ice land and life.
For example Europes relatively mild climate is maintained in part by the large Atlantic current called the Gulf Stream which is experiencing an unprecedented slowdown Changing these currents will have major. Within this Earth system both the physical and biological processes of the ocean play a key role in the water. Even with their vast capacity to absorb heat and carbon dioxide oceans were 017 degrees Celsius 03 degrees Fahrenheit warmer in 2017 than in 2000 and the warming trend appears to be accelerating.
Higher acidity is harmful to coral and other marine life. Oceanic heat is released more slowly than on land keeping coastal. In a conversation with a University of Queensland marine biologist Jackson learns how science has only recently connected climate change with ocean acidification.
As the oceans change due to climate alterations rain and snowfall patterns will shift in response. This would further block the formation of sea ice and disrupt the sinking of denser cold salty water. The ocean is a significant influence on Earths weather and climate.
Our seas contain 60 times more carbon than the atmosphere and they can release it at sufficiently rapid rates to cause dramatic changes in the climate. Warmer and more acidic oceans are likely to disrupt coastal and marine ecosystems. One way that the worlds ocean affects weather and climate is by playing an important role in keeping our planet warm.
This causes changes in water temperature ocean acidification and deoxygenation leading to changes in oceanic circulation and chemistry rising sea levels increased storm intensity as well as. The ocean plays an important role in shaping our climate and weather patterns. Greater concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere also mean that more.
The oceans are obviously the Earths largest reservoir of moisture. In the summer the ocean acts to cool the land and in the winter the opposite effect occurs and the land is kept warmer. Although this has slowed global warming it is also changing ocean chemistry.
What is less well known outside of scientific circles at least is the role oceans have to play in this. Its huge capacity as a heat and water reservoir moderates the climate of Earth. The second law of thermodynamics dictates that heat moves to a cold sink however and the destination of least resistance for tropical heat is the poles where it melts the icecaps.
The moderating effect of ocean temperature reduces the daily and annual range. Warmer oceans are also one of the main causes of rising sea level. The ocean absorbs CO2 from the atmosphere and the CO2 reacts with seawater increasing the oceans acidity.
They mediate temperature and drive the weather determining rainfall droughts and floods. The ocean and climate change.

Global Climate Change Explorer Oceans And Water Exploratorium

What Role Does The Ocean Play In The Weather

Nasa The Ocean A Driving Force For Weather And Climate Youtube
Climate Crisis And Ocean Warming The Shape Of Life The Story Of The Animal Kingdom
Comments
Post a Comment